User Flow Diagrams - Series & Parallel Connections
Flow Connections in User Interactions
In the world of user experience (UX) design, understanding series and parallel user flow connections in the user flow diagramming phase is crucial for UX designers to create efficient and user-friendly interactive experiences.
Series Connection
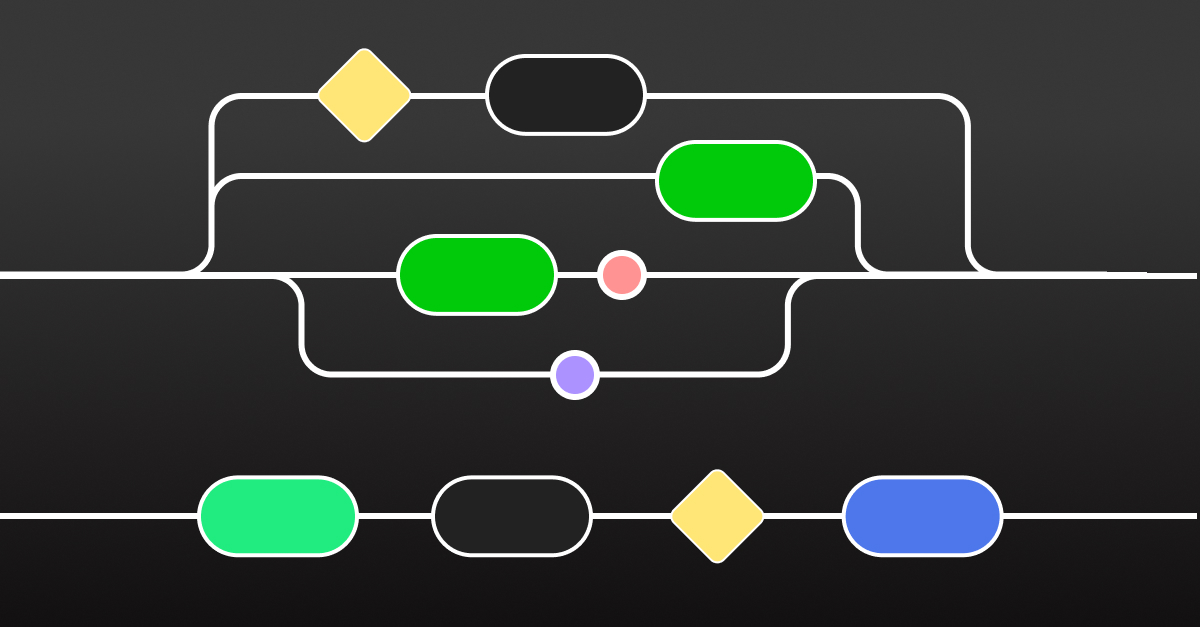
In user flow diagrams, a series connection represents a sequential progression of tasks where each step must be completed before the next can begin. These connections create a linear user journey with discrete, ordered interactions.
Example
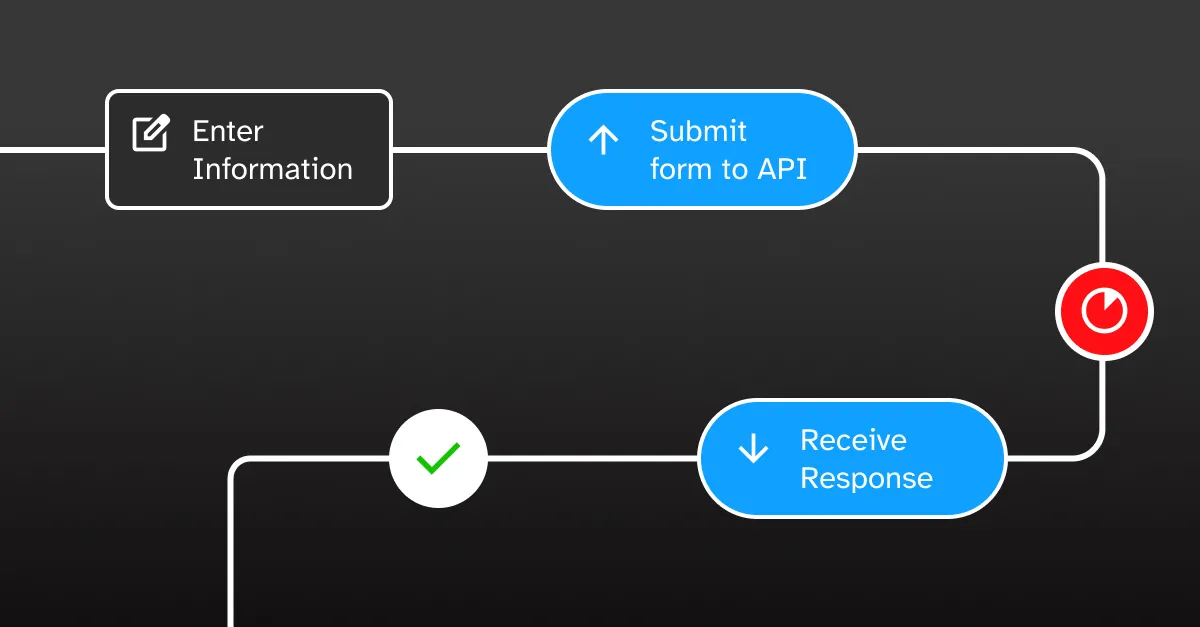
Consider a form submission process where a user must:
- Enter information
- Submit form to API
- Wait for API response
- Receive confirmation
Each task has its own time slot, and the subsequent task cannot start until the previous one is fully completed.
This creates a clear, step-by-step user experience where actions are dependent on each other.
Parallel Connection
Parallel connections in user flow diagrams represent tasks that can run simultaneously or have overlapping execution times. Unlike series connections, parallel tasks can:
- Start at the same time
- Complete at different intervals
- Run concurrently while in progress
Example
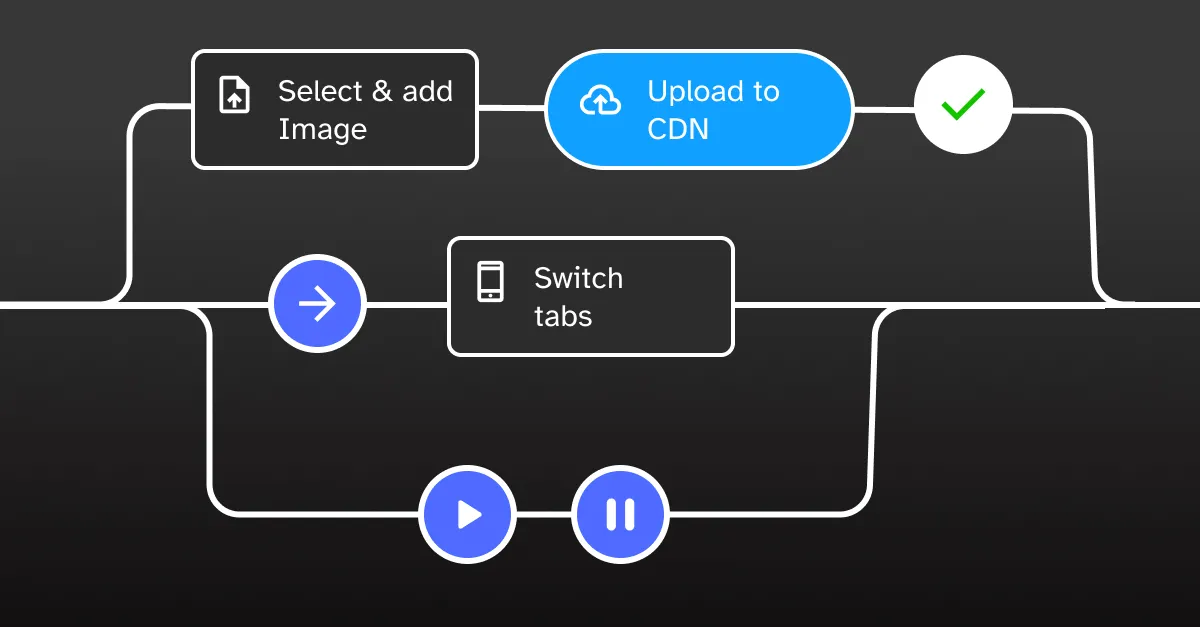
Imagine a mobile app where:
- User uploads a profile picture
- Simultaneously checks notifications
- Begins loading profile settings
These tasks can occur simultaneously, improving perceived performance and user experience.
Gen AI Interactions
With the growing use of Gen AI APIs, response times often vary:
- A simple language translation might take milliseconds
- A complex data analysis, image could take several seconds
- A generative AI task, like image and video creation, might require extended processing
With AI, managing interactions goes beyond mere functional efficiency—it’s about crafting experiences that feel intelligent, responsive, and human. A solid understanding of task execution, whether in series, parallel, or a combination of both, is essential for minimizing perceived wait times and improving the overall user experience.
Example
Currently, it takes almost 30 seconds to generate an image from a complex query, as seen in the example below. As designers, can we reduce the perceived wait time by initiating tasks, threads, or API calls earlier? This is an intriguing problem to tackle, and optimizing the order of execution and interaction will be crucial in minimizing perceived load time and decreasing abandonment rates
Conclusion
Unlocking the potential of series and parallel task flows during the user flow diagramming phase; enables UX designers to create intuitive, streamlined, and captivating digital experiences. By recognizing how tasks intersect, load, and progress, designers can shape interfaces that are both efficient and enjoyable.